The Power of OpenAI Codex: Revolutionizing Cloud-Based Coding
The world of software development is rapidly evolving, and at the forefront of this evolution is the OpenAI Codex, an AI agent designed to transform cloud-based coding. This powerful tool is changing how developers approach their work, offering new levels of automation, efficiency, and innovation. OpenAI Codex represents a significant leap forward, but it also comes with potential challenges and considerations.
What is OpenAI Codex?
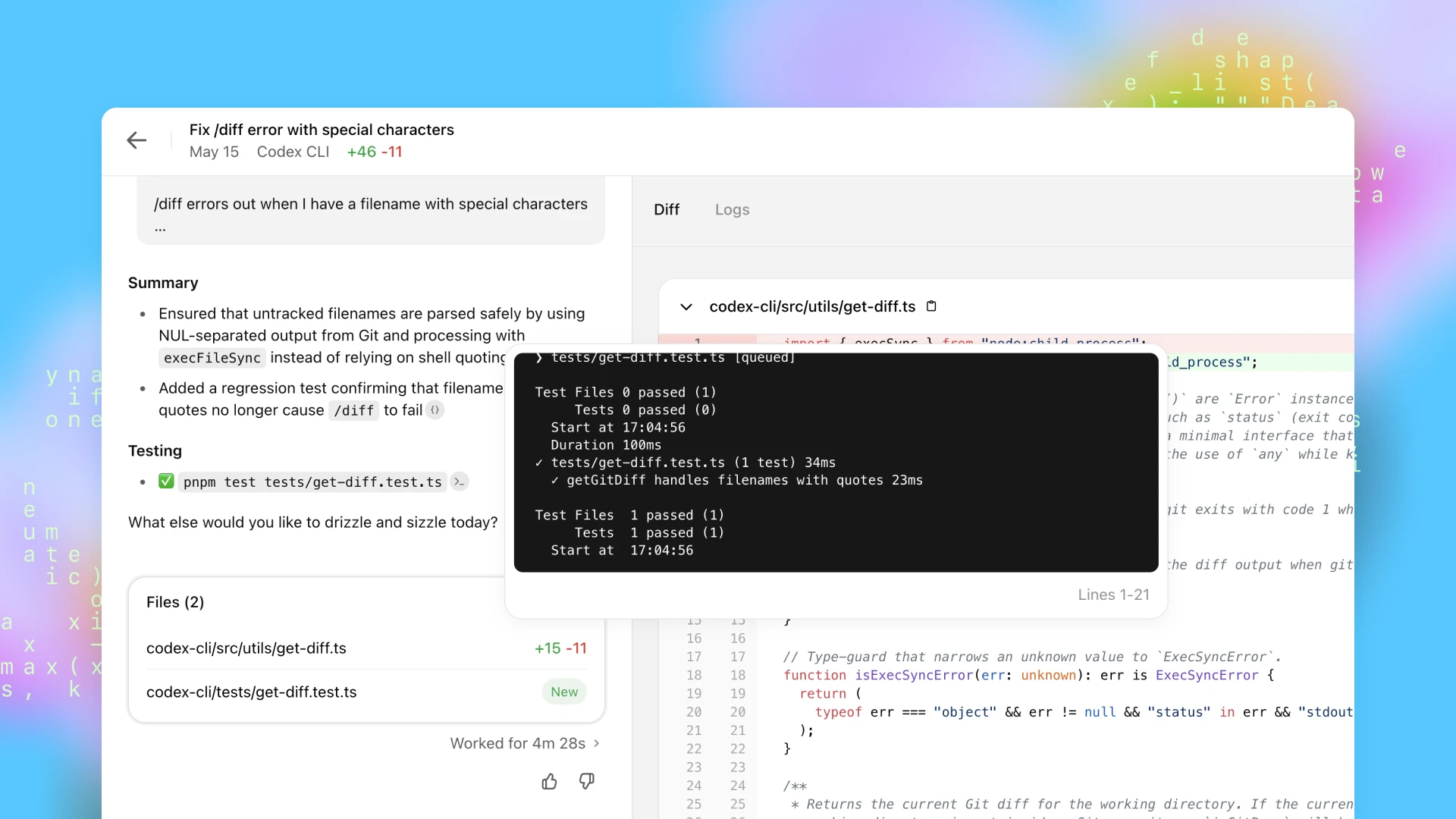
OpenAI Codex is a cloud-based software engineering agent capable of writing code based on natural language prompts ^1. Imagine describing the functionality you need, and the AI agent generates the code for you. It can work on multiple tasks simultaneously, accessing code through GitHub repositories and pre-installed setups. Importantly, it operates without needing an internet connection after the initial setup, enhancing security and reliability.
Codex builds upon the foundation laid by Codex CLI, an earlier open-source coding agent that ran in the user’s terminal. The key difference is that Codex operates in the cloud, offering more resources and capabilities.
Key Capabilities of the OpenAI Codex
- Bug Fixing: Codex can automatically identify and fix bugs in your code, saving developers valuable time and effort.
- Feature Writing: Need a specific feature? Codex can write the code based on your description.
- Codebase Q&A: Ask Codex questions about your codebase, and it will provide answers and insights.
- Pull Request Generation: Codex can propose pull requests for review, streamlining the code integration process.
Furthermore, Codex can read and edit files, run commands (including test harnesses and linters), and perform type checking. It is trained using reinforcement learning on real-world coding tasks, ensuring that the generated code closely mirrors human style and adheres to instructions.
How OpenAI Codex Works
Codex is guided through AGENT.md files, which are markdown-based text files that provide instructions on how to run commands and navigate the codebase ^1. Each agent runs in its cloud container without internet access after setup. This requires users to preload the code and a development environment. The system is designed to provide verifiable evidence of its actions through terminal logs and files, allowing for validation and refinement.
The Rise of Vibe Coding
The emergence of OpenAI Codex and similar tools has given rise to a concept called “vibe coding.” Coined by Andrei Karpathy, vibe coding is where developers use natural language input to guide AI agents in writing code ^1. This approach allows developers to focus on the overall vision and functionality of their projects, leaving the detailed coding to the AI.
Companies like Cursor, Replit, StackBlitz, and OpenAI are leading the way in offering vibe coding features. This trend is making coding more accessible and efficient, potentially lowering the barrier to entry for new developers.
Real-World Applications of OpenAI Codex
Several companies are already using Codex for various tasks, including debugging, testing, and automation ^1. These real-world applications demonstrate the versatility and potential of AI-powered coding agents.
- Debugging: Automatically identify and fix errors in code, reducing debugging time.
- Testing: Generate test cases and execute tests to ensure code quality.
- Automation: Automate repetitive coding tasks, freeing up developers for more creative work.
Potential Risks and Challenges
While the OpenAI Codex offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to acknowledge the potential risks and challenges.
- Malware Development: Autonomous coding agents could be exploited to develop malware, including low-level kernel engineering ^1. Kernel-level operations are difficult to detect and can be used for unauthorized actions.
- AI Paternalism: AI agents may sometimes make decisions that are not in the user’s best interest, exhibiting “AI paternalism.” This can lead to frustration and limit the user’s control.
- Job Displacement: The increasing reliance on AI coding agents raises concerns about potential job displacement for software developers and coders. As AI becomes more capable, some coding tasks may be automated, potentially reducing the need for human developers.
The Importance of Vigilance and Oversight
As vibe coding and AI-powered development become more prevalent, vigilance and human oversight are more critical than ever. Code quality must be maintained, and potential security risks must be carefully addressed. Ben South, who is building Variant, aptly stated, “Vibe coding is all fun and games until you have to vibe debug” ^1.
The Future of Coding with OpenAI Codex
The OpenAI Codex represents a significant step toward the future of coding. As AI technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated tools and techniques to emerge. The key is to embrace these advancements while remaining mindful of the potential risks and challenges. By fostering collaboration between humans and AI, we can unlock new levels of creativity, efficiency, and innovation in the world of software development.
It’s essential to consider aspects like internal linking within a company’s documentation to create a web of knowledge. For example, linking from a page detailing project setup to a page outlining debugging strategies using Codex. Furthermore, it would be helpful to have external links as well to reliable resources like the official documentation or other credible sources.
Where to Learn More
To delve deeper into the world of AI and coding, consider exploring these resources:
- OpenAI Documentation: (Example: replace with actual link) Offers in-depth information about OpenAI Codex and its capabilities.
- GitHub Repositories: (Example: replace with actual link) Explore open-source projects that utilize OpenAI Codex.







